The following is a complete manufacturing process from SMT (surface mount technology) to DIP (dual in-line package), to AI detection and ASSY (assembly), with technical personnel providing guidance throughout the process. This process covers the core links in electronic manufacturing to ensure high-quality and efficient production.
Complete manufacturing process from SMT→DIP→AI inspection→ASSY
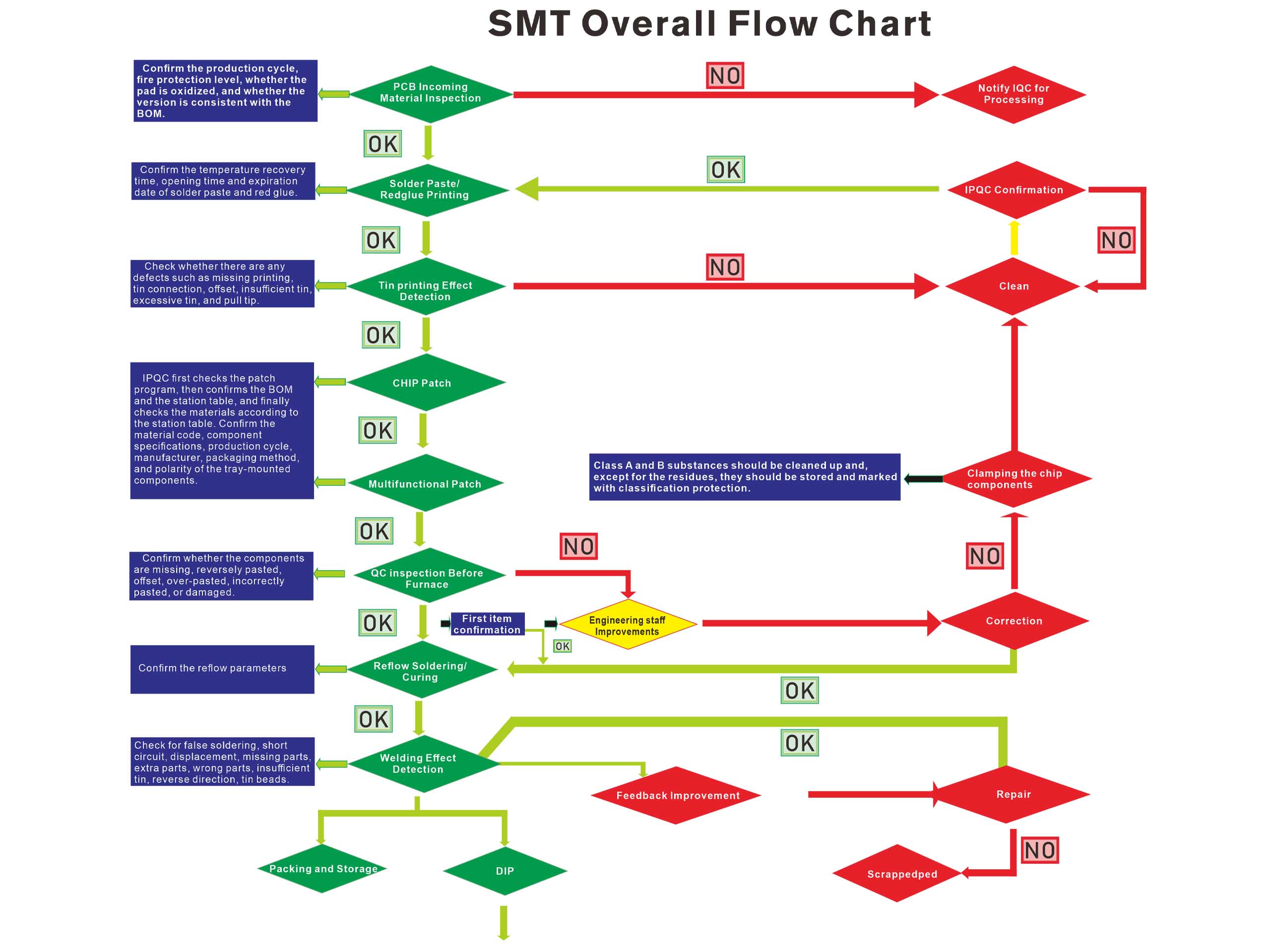
1. SMT (surface mount technology)
SMT is the core process of electronic manufacturing, mainly used to install surface mount components (SMD) on PCB.
(1) Solder paste printing
Equipment: solder paste printer.
Steps:
Fix the PCB on the printer workbench.
Print the solder paste accurately onto the pads of the PCB through the steel mesh.
Check the quality of solder paste printing to ensure that there is no offset, missing printing or overprinting.
Key points:
The viscosity and thickness of the solder paste must meet the requirements.
The steel mesh needs to be cleaned regularly to avoid clogging.
(2) Component placement
Equipment: Pick and Place Machine.
Steps:
Load SMD components into the feeder of the SMD machine.
The SMD machine picks up components through the nozzle and accurately places them on the specified position of the PCB according to the program.
Check the placement accuracy to ensure that there is no offset, wrong parts or missing parts.
Key points:
The polarity and direction of the components must be correct.
The nozzle of the SMD machine needs to be maintained regularly to avoid damage to the components.
(3) Reflow soldering
Equipment: Reflow soldering furnace.
Steps:
Send the mounted PCB into the reflow soldering furnace.
After four stages of preheating, constant temperature, reflow and cooling, the solder paste is melted and a reliable solder joint is formed.
Check the soldering quality to ensure that there are no defects such as cold solder joints, bridging or tombstones.
Key points:
The temperature curve of reflow soldering needs to be optimized according to the characteristics of the solder paste and components.
Calibrate the furnace temperature regularly to ensure stable welding quality.
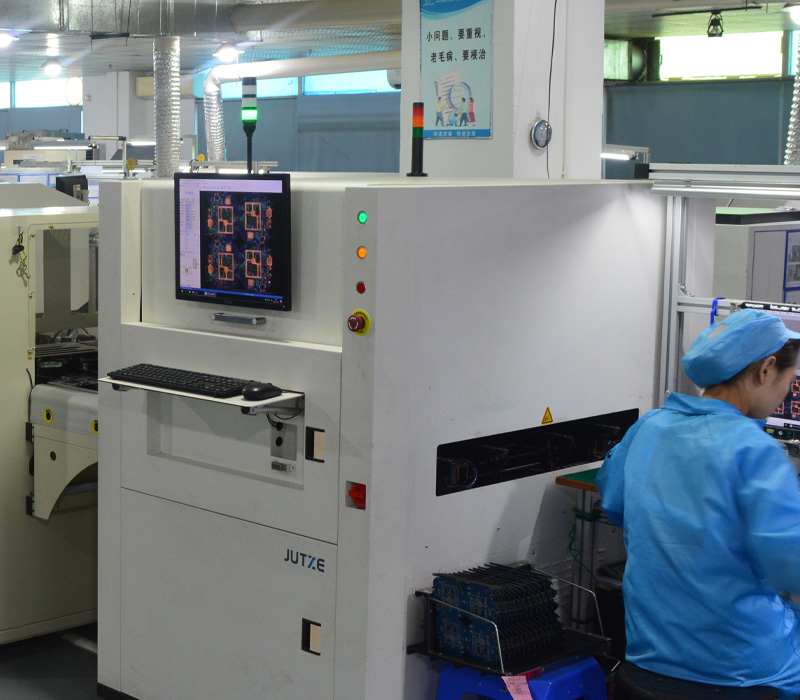
(4) AOI inspection (automatic optical inspection)
Equipment: automatic optical inspection instrument (AOI).
Steps:
Optically scan the soldered PCB to detect the quality of solder joints and component mounting accuracy.
Record and analyze defects and feedback to the previous process for adjustment.
Key points:
The AOI program needs to be optimized according to the PCB design.
Calibrate the equipment regularly to ensure detection accuracy.


2. DIP (dual in-line package) process
The DIP process is mainly used to install through-hole components (THT) and is usually used in combination with SMT process.
(1) Insertion
Equipment: manual or automatic insertion machine.
Steps:
Insert the through-hole component into the specified position of the PCB.
Check the accuracy and stability of component insertion.
Key points:
The pins of the component need to be trimmed to the appropriate length.
Ensure the component polarity is correct.
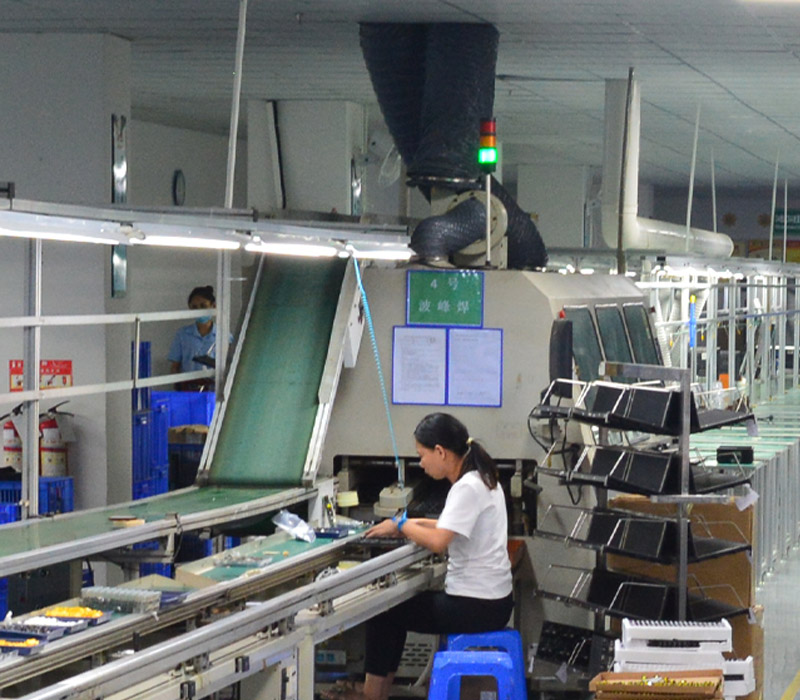
(2) Wave soldering
Equipment: wave soldering furnace.
Steps:
Place the plug-in PCB into the wave soldering furnace.
Solder the component pins to the PCB pads through wave soldering.
Check the soldering quality to ensure there is no cold solder joints, bridging or leaking solder joints.
Key points:
The temperature and speed of wave soldering need to be optimized according to the characteristics of the PCB and components.
Clean the solder bath regularly to prevent impurities from affecting the soldering quality.
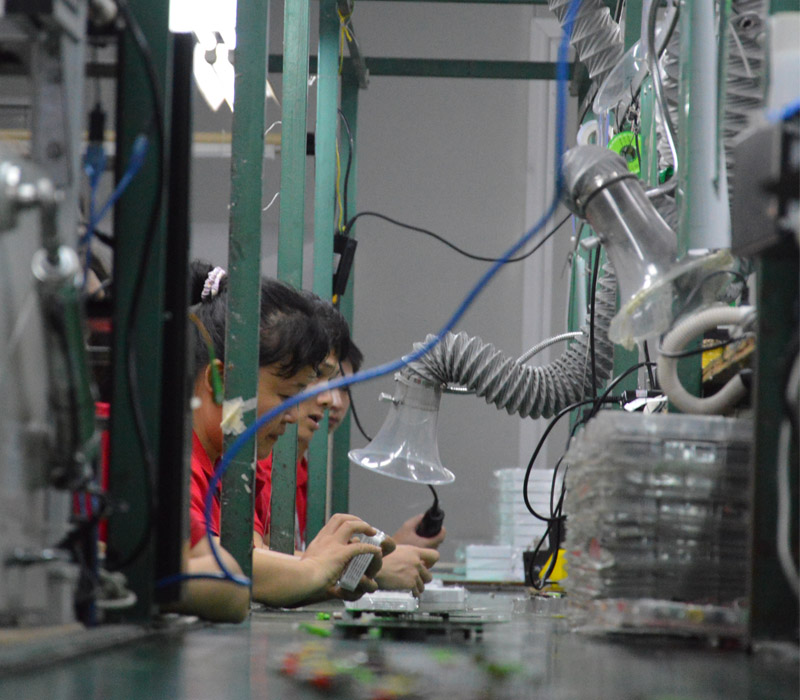
(3) Manual soldering
Manually repair the PCB after wave soldering to repair defects (such as cold solder joints and bridging).
Use a soldering iron or hot air gun for local soldering.
3. AI detection (artificial intelligence detection)
AI detection is used to improve the efficiency and accuracy of quality detection.
(1) AI visual detection
Equipment: AI visual detection system.
Steps:
Capture high-definition images of the PCB.
Analyze the image through AI algorithms to identify soldering defects, component offset and other problems.
Generate a test report and feed it back to the production process.
Key points:
The AI model needs to be trained and optimized based on actual production data.
Update the AI algorithm regularly to improve the detection accuracy.
(2) Functional testing
Equipment: Automated test equipment (ATE).
Steps:
Perform electrical performance tests on the PCB to ensure normal functions.
Record test results and analyze the causes of defective products.
Key points:
The test procedure needs to be designed according to product characteristics.
Regularly calibrate the test equipment to ensure test accuracy.
4. ASSY process
ASSY is the process of assembling PCB and other components into a complete product.
(1) Mechanical assembly
Steps:
Install the PCB into the housing or bracket.
Connect other components such as cables, buttons, and display screens.
Key points:
Ensure assembly accuracy to avoid damage to the PCB or other components.
Use anti-static tools to prevent static damage.
(2) Software burning
Steps:
Burn the firmware or software into the memory of the PCB.
Check the burning results to ensure that the software runs normally.
Key points:
The burning program must match the hardware version.
Ensure that the burning environment is stable to avoid interruptions.
(3) Whole machine testing
Steps:
Perform functional tests on the assembled products.
Check the appearance, performance and reliability.
Key points:
The test items must cover all functions.
Record test data and generate quality reports.
(4) Packaging and shipment
Steps:
Anti-static packaging of qualified products.
Label, pack and prepare for shipment.
Key points:
Packaging must meet transportation and storage requirements.
Record shipping information for easy traceability.

5. Key points
Environmental control:
Prevent static electricity and use anti-static equipment and tools.
Equipment maintenance:
Regularly maintain and calibrate equipment such as printers, placement machines, reflow ovens, wave soldering ovens, etc.
Process optimization:
Optimize process parameters according to actual production conditions.
Quality control:
Each process must undergo strict quality inspection to ensure yield.








